ニュージーランドの政治
ニュージーランドの政治は、単一の議会制代議制民主主義の枠組みの中で機能しています。ニュージーランドは立憲君主制で、1952年2月6日以降、エリザベス女王2世が主権者であり国家元首となっています。
ニュージーランド議会は立法権を持ち、女王と代議院で構成されています。女王がニュージーランドにいないときは、ニュージーランド総督が代理を務めます。代議院議員は通常3年ごとに選出されます。ニュージーランドの立法慣行の多くは、英国のウェストミンスター議会の不文律や先例に由来しています。少数与党の政府は一般的であり、典型的には他の政党との信頼と供給の合意に依存しています。国は、複数の政党システムを持っていますが、ニュージーランドの支配的な政党は、歴史的に労働党と国民党(またはその前身)であるされています。
ニュージーランドの行政権は、「女王は君臨するが、政府が統治する」という原則に基づいています。女王とその総督は、政治的に中立な立場にあり、統治の日常的な側面には関与しませんが、政府のプロセスには不可欠な存在です。閣僚は、民主的に選出された代議院議員の中から選ばれます。ほとんどの大臣は、ニュージーランド政府の主要な意思決定機関である内閣に所属しています。首相は、最上級の大臣であり、内閣の議長であり、つまり政府のトップです。その他の大臣は、首相の助言に基づいて総督が任命し、すべて議会に責任を負います。
エコノミスト・インテリジェンス・ユニット(英国の調査機関)は、2016年にニュージーランドを「完全な民主主義国」と評価しました。ニュージーランドは政府の透明性が高く、汚職の認知度は世界で最も低いとされています。
MMP選挙制度
MMPは、現在ニュージーランドで導入されている選挙制度です。MMPは「Mixed Member Proportional(小選挙区比例代表併用
制)」の略です。政党は、できるだけ多くの議席を獲得したいと考えています。人々は投票の際に、自分が住んでいる地域を代表してほしい人を選んでいるのです。最も多くの票を獲得した候補者が当選し、国会議員となります。
政府の各部門
立法府
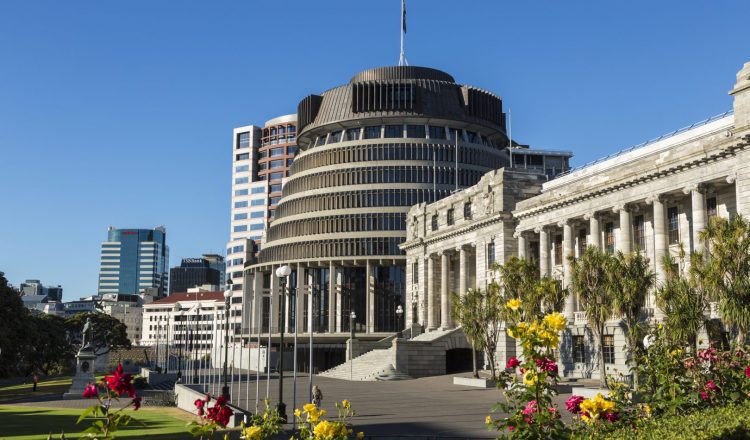
国会は、法律の制定、国家予算の採択、行政政府の統制を行います。現在は代議院の一院制です。1951年以前は、第二院である上院がありました。代議院はウェリントンの国会議事堂で開かれます。
国会議事堂は代議院の本拠地であり、法律はまず法案として代議院に提出される。議会法(法定法)になる前に、代議院と総督による承認プロセスを経なければなりません。
議員は国会議員(Member of Parliament:MP)と呼ばれています。国会議員の任期は最長で3年ですが、例外的な状況下では早期に選挙が行われることもあります。18歳以上の永住権保持者であればほぼ共通の参政権が与えられており、女性は1893年に選挙権を獲得しました。他の多くの議会制政府と同様に、行政機関(「政府」と呼ばれる)は議会から選出され、議会に対して責任を負います。例えば、不信任案が可決された場合、政府は辞任するか、議会解散と早期総選挙を求めることになります。
行政機関
エリザベス女王2世は、ニュージーランドの主権者であり、国家元首です。女王は通常ニュージーランドに居住していないため、君主制の機能は女王の代理人である総督が担っています。2017年現在、総督はデイム・パツィー・レディです。総督は正式には、内閣の任免権、議会の解散権、代議院での可決後にロイヤルアセントで法案を否決または署名する権限を持っています。行政評議会は、全閣僚で構成される正式な委員会で、特権的な権限の行使について総督に助言をします。行政評議会のメンバーは、国会議員(MP)であることが義務付けられており、ほとんどのメンバーが内閣にも所属しています。
内閣は最も上級の政策決定機関であり、慣例により最大与党の議会指導者でもある首相が率います。首相は、ニュージーランドの事実上のリーダーであり、形式的には君主に与えられている行政機能(特権的権限)を行使します。内閣に所属する閣僚は、重要な決定を集団で行い、その結果について集団で責任を負うことになります。
総選挙の結果、代議院で過半数の議員の信任(支持)を得られた政党または連立政権が政府を樹立します。2017年9月に行われた直近の総選挙では、労働党は2位に終わりましたが、ニュージーランドファーストとの連立と、緑の党との信任供給協定によって政権をとることができました。ジャシンダ・アーダーン首相率いる第6次労働党政権は、2017年10月26日に総督によって宣誓されました。
2017年以降、国民党は労働党主導の政府の公式野党を形成しています。野党党首は影の内閣(Shadow Cabinet)を率いて、首相が率いる内閣の行動を精査します。議会内の野党は、政府の責任を追及するのに役立ちます。
司法機関
ニュージーランドの司法機関には、4つの基本的なレベルの裁判所があります。
- 最高裁判所
- 控訴裁判所
- 高等裁判所
- 地方裁判所(青年裁判所を含む)です。
最高裁判所は、2003年に制定された最高裁判所法に基づいて2004年に設立され、ロンドンの枢密院に代わってニュージーランドの最後の砦となる裁判所です。高等裁判所は、重大な刑事犯罪や民事問題を扱い、下級裁判所からの控訴を審理します。控訴裁判所は、法律上の問題について高等裁判所からの控訴を審理します。
司法の長である最高裁長官は、首相の助言に基づいて総督が任命し、最高裁判所を統括します。2019年現在、現職の最高裁判事はデイム・ヘレン・ウィンケルマン(Dame Helen Winkelmann)氏。その他の上級裁判所の裁判官は、最高裁長官、検事総長、事務局長の助言に基づいて任命されます。裁判官および司法官は、行政政府からの司法の独立性を維持するために、非政治的に任命され、在職期間に関する厳格な規則が適用されています。裁判官は、資格、個人の資質、関連する経験に基づいて任命されます。裁判官は、不品行が証明された代議院の演説に基づいて検事総長が罷免する場合を除き、罷免されません。
ニュージーランドの法律には、3つの主要な典拠があります。イギリスのコモン・ロー(判例法)、1947年以前に制定されたイギリス議会の一部の法令(特に1689年の権利章典)、そしてニュージーランド議会の法令です。コモン・ローを解釈する際、裁判所は、裁判所はイギリスや関連する国で解釈されているコモンローとの統一性を保つように努めてきました。
国会議員(MP)
国会議員(Members of Parliament:MP)とは、通常、総選挙で国会議員に選出された人たちのことです。
国会議員にはさまざまな役割があります。国会議員の中には、政権を担う政党もあれば、野党の議員もいます。すべての国会議員は、代議院においてニュージーランドの国民の代表です。また、彼らは通常、政党を代表しています。国会議員の任務は以下の通りです。
- ニュージーランドの人々の意見や懸念を表すこと
- 新しい法律の制定と法律の更新
- 税金の使い道の承認
- 政府が賢明で責任ある決定をしているかどうかを確認すること