新西兰政治
新西兰的政治在统一的议会代议制民主框架内运作。新西兰是君主立宪国家,世袭君主 —— 自 1952 年 2 月 6 日以来,伊丽莎白二世女王 —— 是主权和国家元首。
新西兰议会拥有立法权,由女王和众议院组成。女王本人不在新西兰的情况下由总督代表。众议院议员通常每三年当选一次。新西兰的许多立法实践来自英国威斯敏斯特议会的不成文惯例和先例。少数民族政府很普遍,通常依赖于与其他各方的信任和供应协议。该国实行多党制,尽管新西兰历史上占主导地位的政党是工党和国民党(或其前身党)。
新西兰的行政权力基于 “女王统治,但政府规则” 的原则。尽管女王及其总督是政府进程的一个组成部分,但仍然在政治上保持中立,不参与治理的日常方面。部长从众议院民主选举产生的议员中选出。大多数部长都是内阁成员,内阁是新西兰政府的主要决策机构。总理是最高级别的部长、内阁主席,因此也是政府首脑。其他部长由总督根据总理的建议任命,他们都向议会负责。
《经济学人》情报处在 2016 年将新西兰评为 “完全民主国家”。该国在政府透明度方面排名高,是世界上最低的腐败水平。
MMP 投票系统
MMP 是新西兰目前实行的投票系统。MMP 代表 “按比例混合成员”。各政党希望在议会中获得尽可能多的席位。当人们投票时,他们正在选择自己想要代表他们所居住的地区的谁。得票最多的候选人获胜并成为议员。
政府的不同部门
立法机构
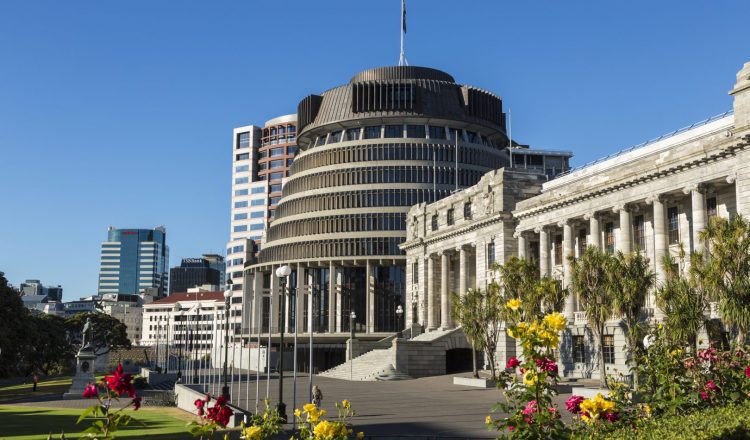
议会负责通过法律、通过国家预算和行使对行政政府的控制权。它目前只有一个分庭,即众议院。1951 年之前,有第二院,立法会。众议院在惠灵顿国会大厦举行会议。
议会大厦是众议院法律首先作为法案提交给众议院的所在地。他们必须经过众议院和总督的批准程序才能成为议会法案 (即成文法)。
立法者被称为议会议员或议员。议会选举的任期最长为三年,但在特殊情况下可以提前举行选举。18 岁及以上的永久居民的选举权几乎是普遍的,女性在 1893 年获得了选票。与许多其他议会政府制度一样,行政机构 (称为 “政府”) 来自议会,并对议会负责 — 例如,成功的不信任动议将迫使政府辞职或寻求解散议会和早日举行大选。
行政部门
伊丽莎白二世女王是新西兰的主权和国家元首。由于女王通常不是新西兰居民,君主制的职能由她的代表总督行使。截至 2017 年,总督是帕西·雷迪夫人。总督正式有权任命和罢免部长以及解散议会;并有权在众议院通过后由皇家同意拒绝或签署法案成为法律。他或她担任行政委员会主席,该委员会是一个由所有部长组成的正式委员会,负责就行使特权向总督提供咨询意见。行政委员会成员必须是议会成员,而且大多数成员也是内阁成员。
内阁是最高级的决策机构,由总理领导,根据惯例,总理也是最大执政党的议会领导人。总理是新西兰事实上的领导人,行使正式赋予君主的行政职能(通过特权)。内阁内部的部长们集体作出重大决定,因此对这些决定的后果负有集体责任。
大选之后,政府由能够赢得众议院多数议员信任(支持)的党或联盟组成。最近一次大选于 2017 年 9 月举行,工党排名第二,但能够通过与新西兰第一的联盟以及与绿党达成信任和供应协议来进行治理。由总理贾辛达·阿登领导的第六届工党政府于 2017 年 10 月 26 日由总督宣誓就职。
自 2017 年以来,国民党成立了劳动力领导的政府的官方反对派。反对党领导人领导一个影子内阁,负责审查由总理领导的内阁的行动。议会内的反对派有助于追究政府的责任。
司法机构
新西兰司法机构有四个基本级别的法院:
- 最高法院;
- 上诉法院;
- 高等法院;
- 和地区法院 (包括青年法院).
最高法院于 2004 年根据 2003 年《最高法院法》成立,取代伦敦枢密院,成为新西兰的终审法院。高等法院处理严重刑事犯罪和民事事务,并审理下级法院的上诉。上诉法院审理高等法院就法律问题提出的上诉。
首席法官、司法机关负责人主持最高法院,由总督根据总理的建议任命。截至 2019 年,现任首席大法官是海伦·温克尔曼夫人。所有其他高等法院法官都是根据首席法官、总检察长和检察长的建议任命的。法官和司法官员是根据严格的任期规则任命的非政治性的,以帮助维持司法独立于行政政府。法官是根据其资格、个人素质和相关经验任命的。除非总检察长根据众议院的发言,因证明行为不当,否则不得免除法官职务。
新西兰法律有三个主要来源:英国普通法、1947 年之前颁布的联合王国议会的某些法规(特别是 1689 年《权利法案》)和新西兰议会的章程。在解释普通法时,法院努力保持与联合王国和相关司法管辖区解释的普通法的统一性。
议员(议员)
议员或议员是被选入议会的人,通常是在大选中。
议员有许多不同的角色。一些议员在政府、政党或政党执政,一些议员反对。所有议员都是众议院中新西兰公众的代表。他们通常也代表一个政党。他们的职责包括:
- 代表新西兰人民的观点和关切
- 制定新法律和更新法律
- 批准税款的使用方式
- 检查政府可以作出明智而负责的决定。