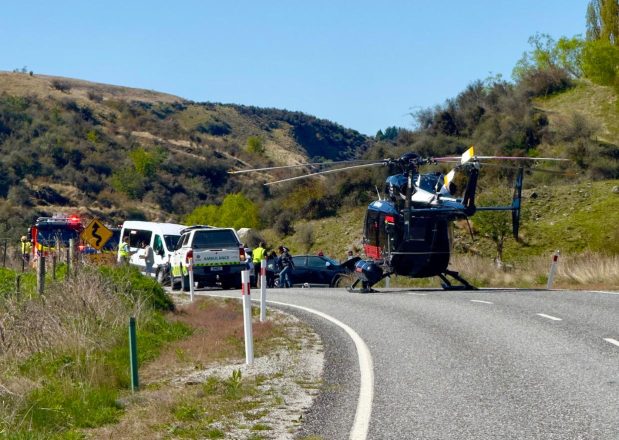
Ang Pebrero 2024 ang pinakamainit na Pebrero na naitala, ayon sa serbisyo sa klima ng EU. Ito ang ikasiyam na magkakasunod na buwan ng mga rekord na temperatura. Mula Hunyo 2023, ang bawat buwan ay nagtakda ng mga bagong mataas na temperatura para sa kani-kanilang mga oras ng taon.
Ang ibabaw ng dagat sa mundo ay nasa pinakamainit din nitong naitala, at ang Antarctic sea ice ay umabot sa napakabababang antas. Habang ang kaganapan sa panahon ng Pasipiko sa El Niño ay nag-ambag sa mga temperaturang ito, ang pagbabago ng klima na sanhi ng tao ang pangunahing sanhi.
“Ang mga gasong Greenhouse na nagtataglay ng init ang pangunahing salarin,” sabi ni Prof Celeste Saulo, Kalihim Heneral ng World Meteorological Organization. Ang mga antas ng carbon dioxide ay nasa pinakamataas nila sa hindi bababa sa dalawang milyong taon, at tumaas nang malaki ang mga ito sa nakaraang taon.
Ang mga gas na ito ay ginawang mas mainit ang Pebrero 2024 tungkol sa 1.77C kaysa sa mga oras bago simulan ang mga tao na magsunog ng malaking halaga ng mga potassium fuel. Sinira ng temperatura na ito ang nakaraang record mula sa 2016 sa paligid ng 0.12C. Ang init ay partikular na matindi sa kanlurang Australia, timog-silangang Asya, timog Africa, at Timog Amerika.
Ang average na temperatura sa nakalipas na 12 buwan ay 1.56C na ngayon higit sa mga antas ng pre-industrial. Noong 2015, halos 200 mga bansa ay sumang-ayon na subukang panatilihin ang pandaigdigang pagtaas ng temperatura sa ibaba ng 1.5C upang maiwasan ang matinding epekto sa klima. Bagama’t hindi pa nasira ang limitasyong ito, ipinapakita ng patuloy na nag-record na temperatura kung gaano kalapit ang mundo sa paggawa nito.
Bilang karagdagan sa temperatura ng hangin, ang iba pang mga sukat ng klima ay nasa mga antas din ng record. Ang isang makabuluhang halimbawa ay ang temperatura ng ibabaw ng dagat Ang pagtaas na ito sa init ng karagatan ay hindi lamang dahil sa El Niño, ngunit patuloy na naging mataas sa nakaraang 10 buwan. Ito ay may kaugnayan dahil maaari itong humantong sa mass pagpaputi ng mga coral reef, pagtaas ng antas ng dagat, at mas matinding bagyo.
Ang kaganapan ng El Niño noong 2023-24, isa sa limang pinakamalakas na naitala, ay unti-unting humina. Patuloy itong makakaapekto sa temperatura at mga pattern ng panahon para sa susunod na ilang buwan, ngunit inaasahang lumipat sa mga neutral na kondisyon sa pagitan ng Abril at Hunyo, at pagkatapos ay sa isang mas malamig na yugto na kilala bilang La Niña sa pagitan ng Hunyo at Agosto. Maaari itong pansamantalang palamig ng pandaigdigang temperatura ng hangin.
Gayunpaman, kung patuloy na naglalabas ng mga aktibidad ng tao ang malaking halaga ng mga Greenhouse gas, patuloy na tumataas ang temperatura sa mahabang panahon, na humahantong sa higit na mga rekord na temperatura at matinding panahon. “Kailangan nating ihinto ang pagsunog ng mga mineral na gasolina at palitan ang mga ito ng mas napapanatiling, nababagong mapagkukunan ng enerhiya,” sabi ni Dr Friederike Otto, senior lektor sa agham sa klima sa Imperial College London. “Hanggang magawa natin iyon, ang matinding mga kaganapan sa panahon na pinalakas ng pagbabago ng klima ay patuloy na sirain ang buhay at pamumuhay.”