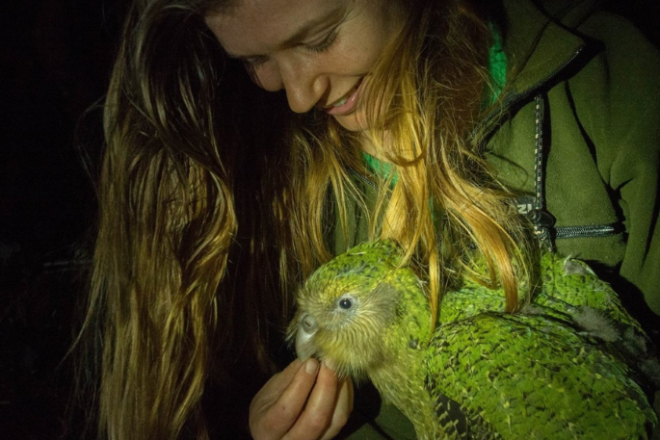
세계에서 유일하게 날지 못하는 앵무새인 카카포는 한때 뉴질랜드 아오테아로아 삼림 곳곳에서 서식했다.
그러나 초기 유럽 관찰자들은 조류 개체수가 일생 동안 급격히 감소하는 것을 보고 이것이 유럽의 야생 개와 다른 포유류 포식자 무리 때문이라고 추측했습니다.
마나아키 웨누아 (Manaaki Whenua) – 랜드케어 리서치 연구원인 조 카펜터 (Jo Carpenter) 박사가 주도한 새로운 연구는 멸종의 역동적인 과정을 더 잘 이해하기 위해 고안되었으며, 카카포의 종말에 가까운 쇠퇴를 초래한 원인에 대해 새로운 시각을 제시했다.
카펜터 박사와 공동 저자인 자넷 윌름스허스트 박사, 마나아키 훼누아 – 랜드케어 리서치, 오클랜드 대학교의 조지 페리 교수는 화석과 1769년 이후의 역사 기록을 독특하게 조합하여 시간의 흐름에 따라 카카포 분포가 어떻게 변했는지 조사했다.
이 데이터는 북섬에서는 1936년에서 1959년 사이, 남섬에서는 1990년에서 2006년 사이인 카카포의 멸종 가능성이 있는 날짜를 예측하는 데 사용되었는데, 이는 약 31~70년의 시차였습니다.연구자들은 이러한 시간 지연이 다양한 선사 시대 사냥과 포식 압력, 북섬과 남섬에서의 서식지 변화 정도에 따른 것이라고 설명합니다.
역사 시대에는 야생 개 무리가 카카포 쇠퇴의 덜 중요한 원동력인 것처럼 보였다.
“카카포는 1913년 남섬에서 야생견이 마지막으로 관찰된 이후 최대 70년 동안 남섬에서 살아남았습니다.”
반대로 유럽에 유입된 구루류, 주머니쥐, 고양이, 노르웨이, 배쥐에 대해서는 탐험가들이 옳았는데, 유럽인이 들어온 이래로 카카포 쇠퇴에 훨씬 더 중요한 영향을 미쳤다.
1995년, 카카포 개체수는 알려진 개체 수 51명까지 줄었습니다.
크레딧: sunlive.co.nz